The Power of Animal Protein and Fat Based Diet
Explore the science-backed benefits of a diet rich in animal protein and fat, from muscle retention to improved energy levels. Learn how foods like steak, eggs, and raw milk can transform your health, and discover practical tips for incorporating these nutrient-dense options into your daily meals.
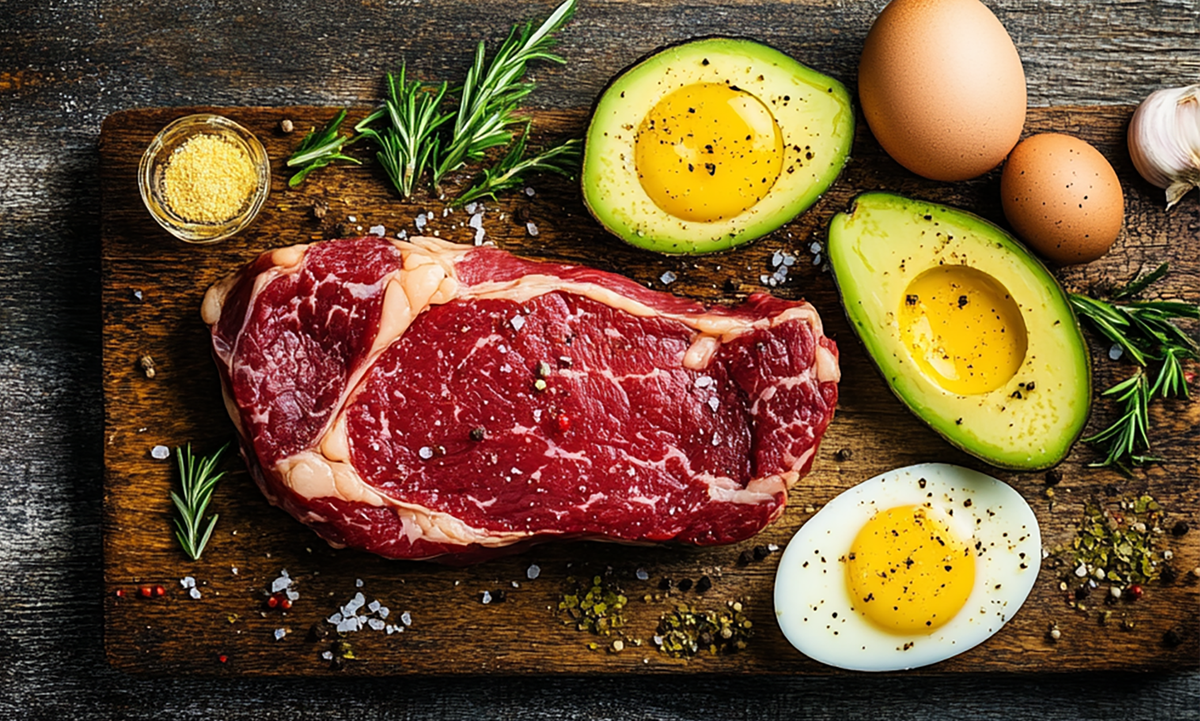

In a world where diet trends come and go, one approach has stood the test of time: a diet rich in animal protein and fat. From steak and eggs to nutrient-dense raw milk, this way of eating has been praised not only for its weight loss benefits but also for its ability to support overall health. But what makes this diet so effective? And how can you incorporate it into your daily meals without sacrificing flavor or variety?
In this article, we’ll explore the science-backed health benefits of a diet high in animal protein and fat, including its role in promoting satiety, supporting muscle retention, and providing essential nutrients. We’ll also discuss how adding complementary foods like fruits, honey, and raw milk can enhance the nutritional profile of this diet.
Health Benefits of a Diet High in Animal Protein and Fat
A diet primarily consisting of animal protein and fat, such as steak and eggs, can offer several health benefits, particularly for weight loss and overall health:
High Protein Content:
- Satiety and Hunger Control: High levels of protein in steak and eggs promote a feeling of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight loss.
- Muscle Retention: Protein is essential for maintaining lean muscle mass, especially during periods of weight loss. This helps in preserving metabolic rate and overall body composition.
Healthy Fats:
- Saturated Fat: Contrary to common misconceptions, recent studies indicate that saturated animal fats, such as those found in steak, are not significantly associated with heart disease, stroke, diabetes, or cancer . In fact, they provide highly bioavailable nutrients and are associated with markers of health, fertility, and longevity.
- Essential Fatty Acids: Animal fats provide essential fatty acids that support various metabolic processes and promote overall health.
Weight Loss:
- Low Carbohydrate Intake: The low carbohydrate content of a steak and eggs diet can lead to reduced blood sugar levels and improved insulin sensitivity, which may enhance energy levels and mental clarity.
- Ketosis: The diet can induce ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates, leading to more efficient fat loss.
Nutrient-Rich:
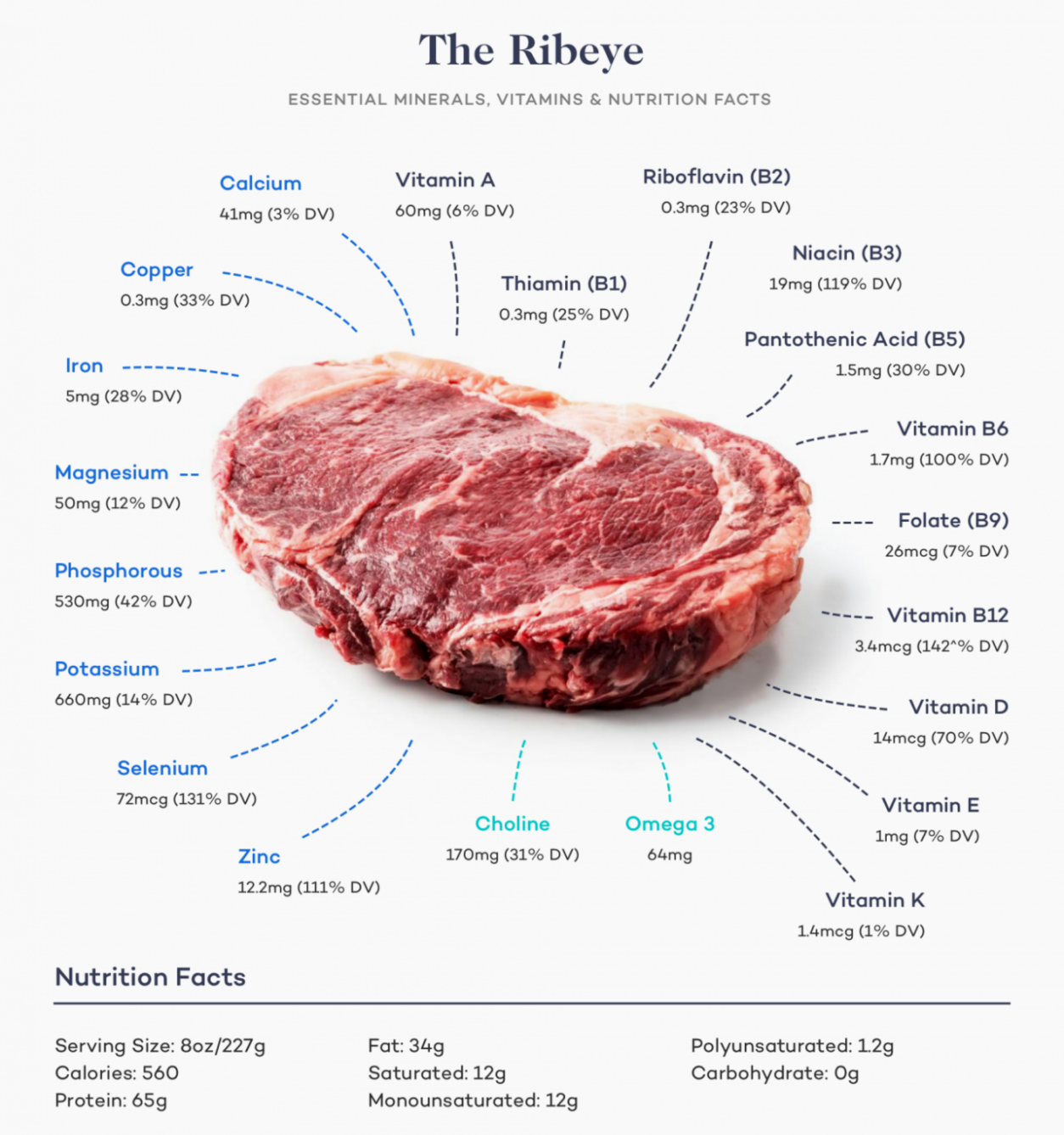
- Vitamins and Minerals: Steak and eggs are rich in essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, vitamin B12, and choline. These nutrients are crucial for red blood cell formation, immune function, and neurological health.

Debunking the Myths Around Saturated Fat
While saturated fats from animal sources have long been vilified, recent studies suggest they are not significantly linked to heart disease, stroke, or diabetes when consumed as part of a balanced diet. In fact, these fats provide essential nutrients like fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, K2) and support hormone production. However, individual responses to saturated fat can vary—those with specific health conditions, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, may need to moderate their intake. The key takeaway? Focus on quality sources, like grass-fed beef and pasture-raised eggs, and listen to your body’s unique needs.
Complementing with Fruits, Honey, and Raw Milk
While a diet high in animal protein and fat can be beneficial, incorporating some fruits, honey, and raw milk can enhance its health benefits:
Fruits:
- Vitamins and Minerals: Fruits are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can complement the nutrient profile of a steak and eggs diet. They provide essential micronutrients that may be lacking in a predominantly animal-based diet.
- Fiber: Fruits are a good source of dietary fiber, which promotes digestive health and helps in maintaining regular bowel movements
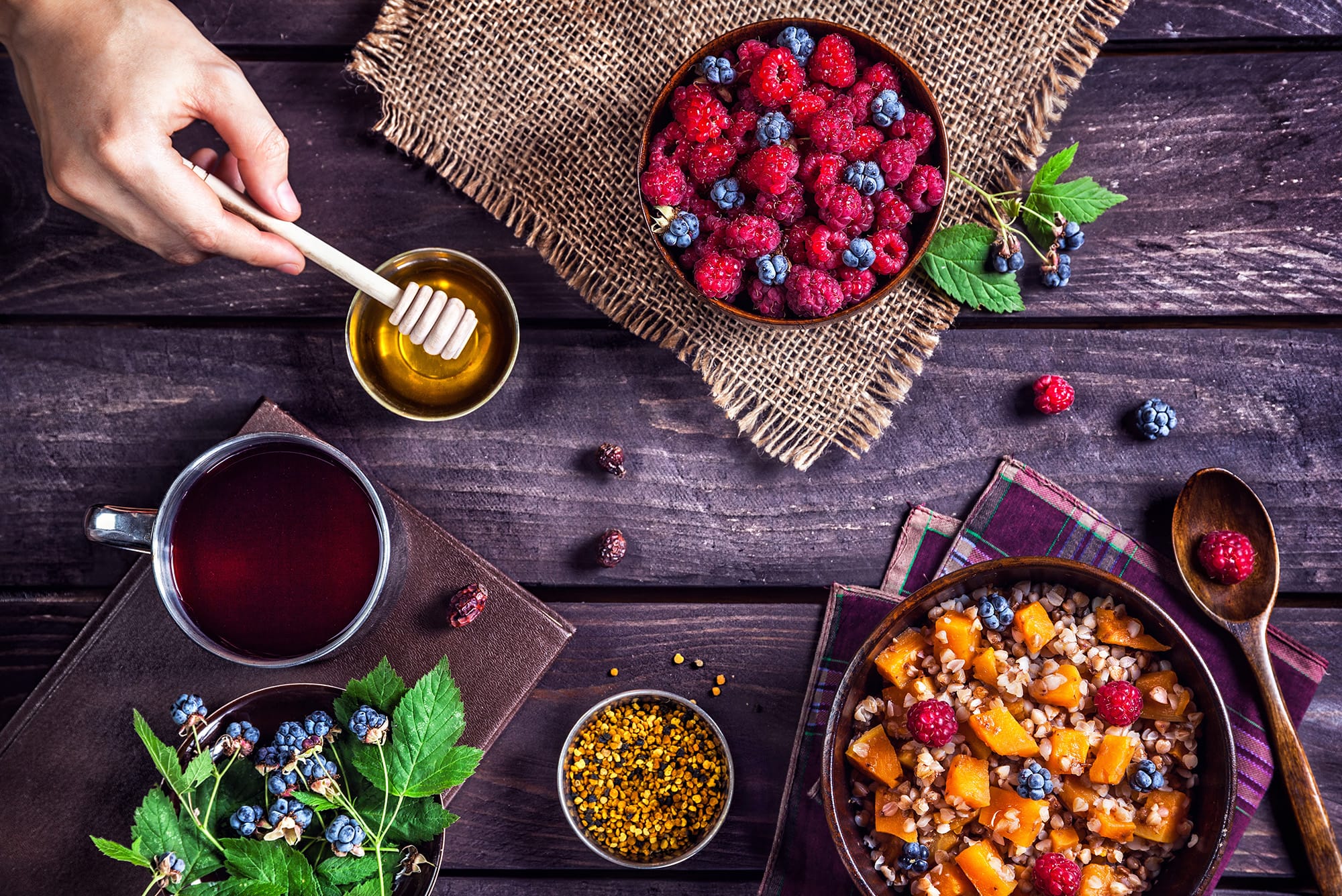

Honey:
- Natural Sweetener: Honey is a natural sweetener that can be used in moderation to add flavor without the negative effects of refined sugars. It contains antioxidants and has antimicrobial properties
- Energy Boost: Honey provides a quick source of energy, which can be beneficial for individuals who need a quick energy boost, especially during physical activities
Raw Milk:
- Nutrient-Rich: Raw milk contains a wide range of nutrients, including calcium, magnesium, and vitamins A, D, and K2. These nutrients support bone health and overall well-being
- Probiotics: Raw milk contains beneficial bacteria that can support gut health and improve digestion
Choosing Ethical and Eco-Friendly Options
The environmental impact of animal-based diets is a growing concern, but sustainable sourcing practices can make a difference. Grass-fed beef, pasture-raised eggs, and locally sourced ingredients not only enhance nutritional quality but also reduce the carbon footprint associated with industrial farming. At Pingu’s Burger, we prioritize partnerships with local farmers who use ethical and sustainable methods, ensuring that every bite supports both your health and the planet. By choosing responsibly sourced animal products, you can enjoy the benefits of this diet while contributing to a healthier ecosystem.

Simple Ways to Incorporate Animal Protein and Fat Into Your Day
Building meals around animal protein and fat doesn’t have to be complicated. For breakfast, try a grass-fed steak paired with avocado and fresh berries for a nutrient-packed start. Lunch could include a hearty burger loaded with fresh veggies and guacamole, while dinner might feature slow-cooked short ribs served with roasted vegetables. Snacks like hard-boiled eggs, nuts, or a whey protein milkshake keep you fueled throughout the day. The key is to combine high-quality animal proteins with complementary foods like fruits, honey, or raw milk for a well-rounded approach.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
While animal protein is highly satiating, portion control remains important to avoid overconsumption of calories. The general guideline for protein intake is about 0.8–1 gram of protein per pound of body weight, depending on activity level and goals. For example, an active adult weighing 150 pounds might aim for 120–150 grams of protein daily. To maintain balance, pair your protein-rich meals with nutrient-dense sides like fresh vegetables or fruits. This ensures you’re meeting your macronutrient needs without exceeding your caloric requirements.
Why Gut Health Matters in Your Diet
Animal-based diets can play a surprising role in supporting gut health, especially when raw milk or fermented foods are included. Raw milk contains probiotics that promote a diverse gut microbiome, which is essential for digestion, immune function, and even mental health. Additionally, healthy fats from animal sources, like butter or egg yolks, provide butyrate—a compound that nourishes gut lining cells. By incorporating gut-friendly foods alongside animal proteins, you create a diet that supports both physical and mental well-being.

What Is Ketosis, and How Can It Benefit You?
Ketosis occurs when your body shifts from burning carbohydrates to burning fat for energy—a state often achieved through low-carb, high-fat diets like those rich in animal protein. This metabolic switch can lead to more efficient fat loss, improved mental clarity, and stabilized energy levels. However, ketosis isn’t suitable for everyone, particularly individuals with certain medical conditions or high-energy demands. If you’re considering this approach, consult a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with your health goals and lifestyle.
Unlocking the Power of Bioavailable Nutrients
One of the standout benefits of animal-based diets is the bioavailability of essential micronutrients. Unlike plant-based sources, which often contain anti-nutrients like phytates, animal proteins provide highly absorbable forms of iron, zinc, vitamin B12, and choline. These nutrients are crucial for red blood cell formation, immune function, and brain health. For example, a single serving of grass-fed beef delivers a concentrated dose of heme iron, which is far more efficiently absorbed than non-heme iron from plants. By prioritizing nutrient-dense animal foods, you can optimize your overall health and vitality.

Tailoring Your Diet to Fit Your Unique Needs
No single diet works for everyone, and the same holds true for a diet high in animal protein and fat. Factors like age, activity level, metabolic health, and personal preferences should guide your food choices. For instance, athletes may require higher protein intake to support muscle recovery, while sedentary individuals might focus on portion control to avoid excess calories. Similarly, those with specific health conditions should work with a healthcare provider to customize their approach. The beauty of this dietary framework lies in its flexibility—adapt it to suit your goals and enjoy the benefits of smarter eating.
How Pingu’s Burger Brings the Science of Animal Protein and Fat to Your Plate
At Pingu’s Burger, we believe that fast food doesn’t have to compromise on nutrition. Our menu is designed to reflect the principles of a diet high in animal protein and fat, while still offering variety and balance. Here are some examples of how you can enjoy these health benefits at Pingu’s:
- Grass-Fed Beef Burgers
Our grass-fed beef patties are packed with high-quality protein, iron, zinc, and B vitamins—nutrients essential for energy, muscle retention, and immune function. Pair one of our burgers with a side of fresh veggies for added fiber and micronutrients. - Protein-Packed Milkshakes
Many of our milkshakes come with an extra scoop of whey protein, making them a perfect post-workout treat or a satisfying snack that supports muscle recovery and satiety. Add a drizzle of honey for natural sweetness and an energy boost. - Slow-Cooked Short Rib Burrito
Our burritos feature tender, slow-cooked short ribs—a rich source of animal protein and healthy fats. Complemented by fresh ingredients like guacamole and homemade sauces, this dish embodies the balance of indulgence and nutrition.
By combining nutrient-dense animal-based proteins with complementary ingredients like fresh fruits, honey, and wholesome sides, Pingu’s Burger proves that eating smart doesn’t mean giving up flavor. Whether you’re looking to lose weight, build muscle, or simply fuel your body with quality nutrients, our menu has something for everyone.
Conclusion
A diet high in animal protein and fat, such as steak and eggs, can be effective for weight loss and overall health due to its high protein content, healthy fats, and essential nutrients. Complementing this diet with fruits, honey, and raw milk can provide additional vitamins, minerals, fiber, and probiotics, enhancing its nutritional value and supporting overall health. However, it is important to maintain a balanced approach and consult a healthcare professional to ensure that all nutritional needs are met.
References
Source: Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
Link: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/
Summary: Explores the role of saturated fats in heart health and debunks common myths about their impact.
Source: British Journal of Nutrition
Link: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition
Summary: Highlights the nutritional advantages of grass-fed beef, including higher omega-3 content and antioxidants.
Source: PubMed Central (PMC)
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5867459/
Summary: A scientific review of ketosis, its benefits for weight loss, and its effects on metabolic health.
Source: National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6044807/
Summary: Discusses the role of probiotics and gut microbiota in supporting digestion, immunity, and mental health.
Source: American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Link: https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/71/5/1233S/4729659
Summary: Examines how animal-based foods provide highly bioavailable nutrients like iron, zinc, and B12.
Source: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
Link: https://www.fao.org/sustainability/en/
Summary: Provides insights into sustainable farming practices and their environmental benefits.
Source: International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN)
Link: https://jissn.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12970-017-0177-8
Summary: Guidelines on optimal protein intake for muscle retention, recovery, and overall health.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
Link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3609166/
Summary: Explores the antimicrobial, antioxidant, and energy-boosting properties of honey.




